
Cisco mac address table ttl default software#
The mac-address-table synchronize command is available from Cisco IOS ® Software Releases 12.2(18)SXE4 and later. Issue these commands in order to enable the synchronization: !- This is a global configuration command and is used to enable the synchronization.Ĭat6K-IOS(config)# mac-address-table synchronize !- This is a privileged EXEC command and is used to clear dynamic MAC addresses.Ĭat6K-IOS# clear mac-address-table dynamic In order to prevent the age out of an entry on a DFC or PFC, even if there is not traffic for that MAC address, enable the MAC address synchronization.

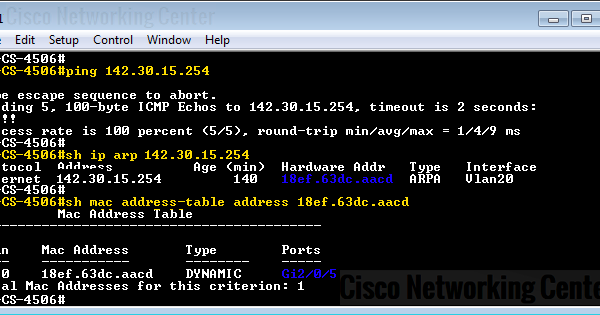
When a MAC address entry is aged out on the PFC, the show mac-address address all command displays the DFC or PFC that holds this MAC address. There are currently two mechanisms available to keep the CAM tables consistent between the different engines, such as DFC (present in line modules) and Policy Feature Card (PFC) (present in supervisor modules): With distributed switching, it is normal that the supervisor engine does not see any traffic for a particular MAC address for a while, so the entry might expire. This means that each DFC learns the MAC address and ages them, which depends on the CAM aging and traffic matching that particular entry. In distributed switching, each Distributed Feature Card (DFC) is responsible for maintaining each own CAM table. Troubleshoot ARP or CAM Related Issues Loss of Dynamic MAC Addresses with Distributed Switching Most switches have multiple TCAMs so that both inbound and outbound security, as well as QoS ACLs, can be evaluated simultaneously, or entirely in parallel with a Layer 2 or Layer 3 forwarding decision. TCAM allows a packet to be evaluated against an entire access list in a single table lookup. Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM)-In multilayer switches, all the processes that access control lists (ACLs) provide in traditional routing, such as matching, filtering, or control specific traffic, are implemented in hardware. If a MAC address is found already present in the table for the correct arrival port, only its timestamp is updated. If a MAC address learned on one switch port has moved to a different port, the MAC address and timestamp are recorded for the most recent arrival port. The port of arrival and the VLAN are both recorded in the table, along with a timestamp. As frames arrive on switch ports, the source MAC addresses are learned and recorded in the CAM table. All hosts within the broadcast domain receive the ARP request, and only Host A responds with its MAC address.ĬAM-All Catalyst switch models use a CAM table for Layer 2 switching. Host B generates a broadcast message for all hosts within the broadcast domain to obtain the MAC address associated with the IP address of Host A. For example, Host B wants to send information to Host A but does not have the MAC address of Host A in its ARP cache. Background InformationĬatalyst switches maintain several types of tables that are tailored for Layer 2 switching or multilayer switching (MLS), and are kept in very fast memory so that many fields within a frame or packet can be compared in parallel.ĪRP-Maps an IP address to a MAC address in order to provide IP communication within a Layer 2 broadcast domain.
Refer to Cisco Technical Tips Conventions for more information on document conventions. This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. There are no specific requirements for this document.
Cisco mac address table ttl default how to#
However we are well beyond that version of IOS, 12.2.18.This document provides information on how to troubleshoot Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) or Content Addressable Memory (CAM) table-related issues on Catalyst 6500/6000 Switches. This bug would allow the global setting to be changed but not impact the individual vlans. What does the statement "Routed MAC aging time: 300 seconds" imply? I did a search on cisco's site and found one reference, indicating that there was a bug in the IOS that was fixed in 12.1.22. No vlan age other than global age configured But on my core switches, (6500 series), after I issue the command and then show the setting, I get the following:
I set the value on all my 3750's and did a show.each vlan shows 14440 as the timeout. Everything I've read on Cisco's site on this matter says to up the cam table time out(mac address aging) to 14400, which matches the arp timeout. I am trying to overcome a unicast flooding problem caused by asymetrical routing, a by product of the server-farm being on one vlan and users on another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
